Understanding Differential Locks in Sustainable Agriculture
Getting stuck in a muddy field or struggling up a steep incline can significantly impact farming efficiency and profitability. Differential locks are a crucial tool for enhancing tractor traction, improving productivity, and minimizing fuel consumption – all essential elements of sustainable agriculture. This guide provides practical, step-by-step instructions on how to effectively and safely use differential locks in various farming scenarios. For more on 4WD tractors, see this resource.
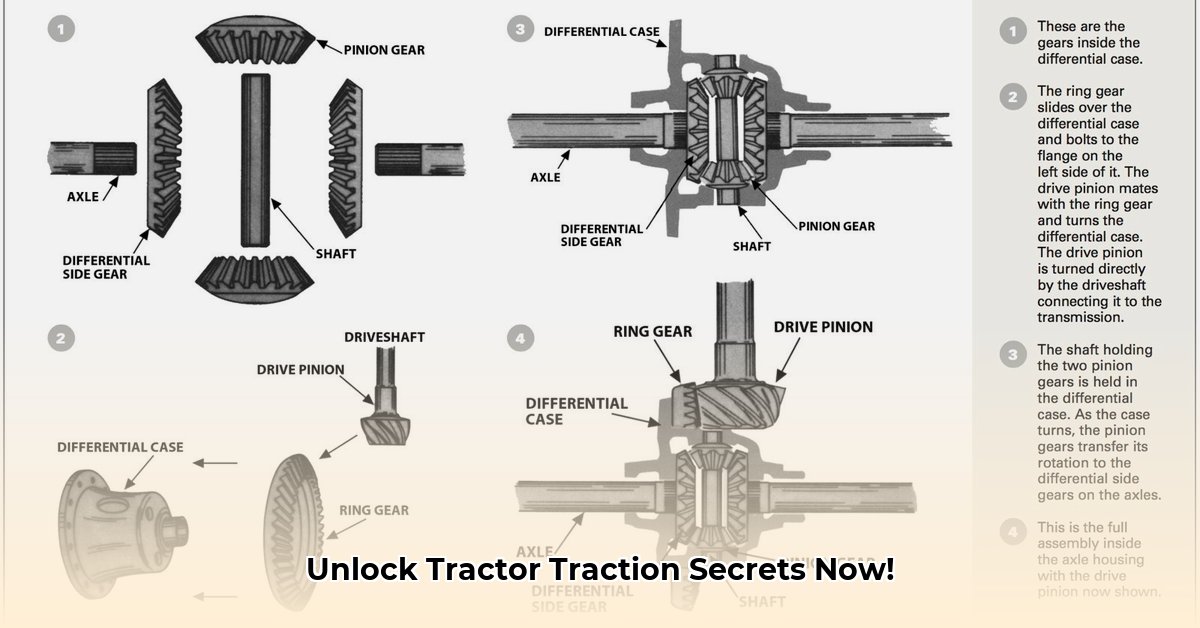
How Differential Locks Work
A tractor's differential allows the rear wheels to rotate at different speeds, essential for turning. However, when one wheel loses traction (e.g., in mud), the other spins freely, resulting in immobility. A differential lock remedies this by forcing both rear wheels to rotate at the same speed. If one wheel slips, power is transferred to the wheel with traction, maintaining forward momentum. Think of it as a "traction amplifier."
Types of Differential Locks
Several types of differential locks cater to different needs and budgets:
- Manual Differential Locks: These require manual engagement, offering simplicity and reliability but demanding driver awareness. They are ideal for farmers who primarily operate on less challenging terrain.
- Automatic Differential Locks: These engage automatically when needed, increasing convenience but potentially adding complexity and cost. This system is frequently found on higher-end tractors.
- Limited-Slip Differentials: These offer improved traction without fully locking the differential, providing a balance between traction and maneuverability. This represents a middle ground in terms of cost and functionality.
Choosing the right type depends on your budget, terrain, and frequency of use. A manual lock might suffice for a smaller farm with mostly clear fields, while an automatic system might be preferred for larger operations with consistently challenging conditions.
When to Use Differential Locks
Differential locks aren't always necessary; unnecessary engagement leads to increased wear and tear. Use them strategically in these situations:
- Steep Inclines: Prevent slippage and ensure safe ascent and descent.
- Muddy or Wet Conditions: Maintain traction on soft, yielding surfaces.
- Snow and Ice: Provide essential grip on slippery surfaces.
- Uneven Terrain: Enhance stability and prevent wheel spin on rough patches.
Remember that proper usage directly minimizes unnecessary wear and tear on your vehicle.
Using Differential Locks Safely and Effectively
Proper use is critical for maximizing benefits and preventing damage:
- Assess Need: Only engage the lock when necessary. Avoid unnecessary engagement.
- Low-Speed Engagement: Engage slowly at low speeds to avoid transmission shock.
- Maintain Moderate Speed: Keep your speed consistent and moderate while the lock is engaged.
- Smooth Disengagement: Disengage the lock gradually once traction is regained.
- Avoid Sudden Stops and Turns: These maneuvers create excessive stress when the lock is engaged.
Proper usage is about maximizing efficiency and minimizing wear.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is vital for longevity and optimal functionality:
- Regular Inspections: Inspect the lock mechanism for wear, damage, or leaks.
- Lubrication: Keep moving parts lubricated per the manufacturer's instructions.
- Listen for Unusual Sounds: Grinding or clicking sounds indicate a problem needing immediate attention.
- Professional Service: Consult a qualified mechanic for any issues.
Preventative maintenance is far less costly than repairs.
Alternatives to Differential Locks
Other traction-enhancing options include:
- All-Wheel Drive (4WD): Provides constant power to all four wheels, offering superior traction but at a higher cost.
- Advanced Tire Technologies: Specialized tires designed for specific terrains (mud, rock, etc.) enhance grip and performance.
The best option depends on the specific farming needs and budget.
Case Study: The Cost of Neglect
A farmer who opted for a lower-cost tractor without a differential lock experienced repeated delays, significant repair costs, and substantial productivity losses. The long-term cost far outweighed the initial savings, emphasizing the importance of thoughtful investment. This highlights the long-term financial benefits of strategically using or investing in differential locks.
Conclusion: Improving Farm Productivity Through Proper Traction
Differential locks are powerful tools that significantly improve tractor traction, leading to increased efficiency, reduced fuel consumption, and ultimately, higher profitability. Safe operation, regular maintenance, and informed decision-making regarding their use and potential alternatives are crucial for successful sustainable agriculture. Remember: proper training and consistent maintenance are essential for optimal performance and longevity.